 Reading Time: 9 minutes
Reading Time: 9 minutes

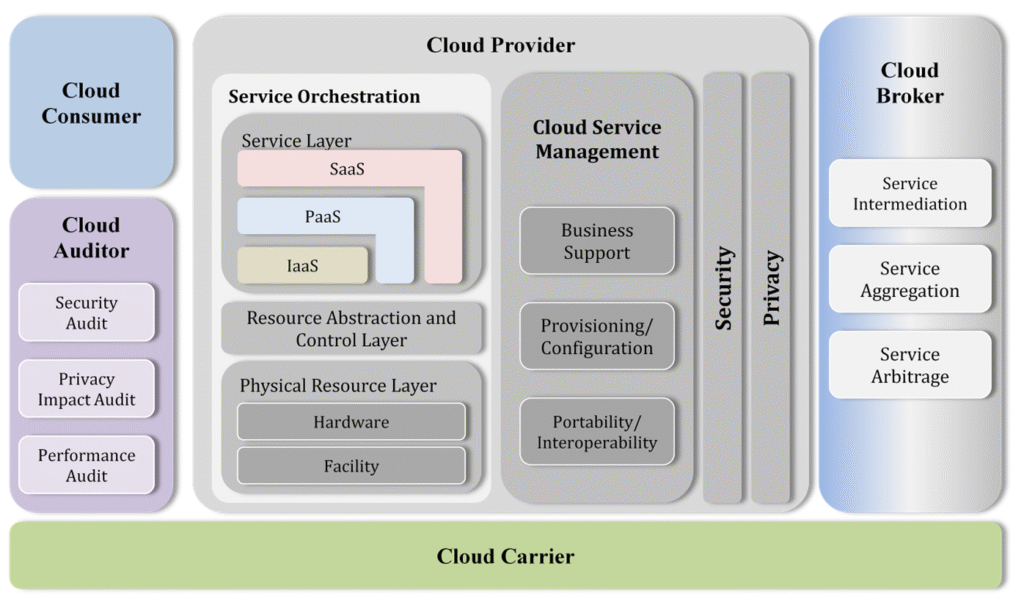
Image Source: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/Legacy/SP/nistspecialpublication500-292.pdf
Cloud computing has become an integral part of modern IT infrastructure, enabling enterprises to achieve scalability, efficiency, and agility. This paper discusses the Cloud Computing Reference Architecture (CCRA), including its key adoption requirements, standard bodies of knowledge (BoK), reference architectures, enterprise suitability, key elements, skill requirements, training, and AI integration possibilities for future interoperability.
1. Key Adoption Requirements on Technologies: for the successful adoption of cloud computing, enterprises must address several technological requirements:
- Infrastructure Readiness: High-speed internet, virtualization capabilities, scalable hardware.
- Security & Compliance: Adherence to standards like ISO 27001, GDPR, and NIST security guidelines.
- Cloud Service Model Selection: Choosing between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS depending on business requirements.
- Automation & Orchestration: Use of Kubernetes, Terraform, or AWS CloudFormation for scalable cloud deployments.
- Interoperability & Integration: Ensuring smooth integration with legacy systems, APIs, and modern cloud-native applications.
2. Best and Standard Bodies of Knowledge (BoK): several bodies provide authoritative guidance for cloud reference architectures:
- The Open Group Cloud Computing Reference Architecture
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cloud Computing Reference Architecture
- ISO/IEC 17788 Cloud Computing Overview
- Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Security Guidelines
- TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) for Enterprise IT
3. Description of BoK Provided Reference Architectures: each BoK defines cloud reference architectures with structured frameworks:
- NIST Cloud Computing Reference Architecture focuses on interoperability, cloud actors, and security models.
- The Open Group Cloud Computing Reference Architecture provides an enterprise-oriented structure for cloud service deployment.
- ISO/IEC 17788 covers cloud computing terminology and conceptual models.
4. Best-Suited Enterprise Reference Architecture: among the various reference architectures, The Open Group Cloud Computing Reference Architecture is ideal for enterprises due to:
- Clear governance models for cloud adoption.
- Multi-cloud interoperability for seamless integration.
- Security-centric approach ensuring compliance and risk management.
5. Key Elements of Cloud Computing Reference Architecture: a well-structured Cloud Computing Reference Architecture consists of:
Actors
- Cloud Consumers
- Cloud Providers
- Cloud Auditors
- Cloud Brokers
- Cloud Carriers
Service Models
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) (Compute, Storage, Networking)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) (Application development, middleware)
- Software as a Service (SaaS) (End-user applications)
Deployment Models
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Multi-Cloud
Functional Components
- Compute & Storage Layers
- Orchestration & Management
- Security & Governance
- Business Analytics & AI Models
Activities
- Provisioning
- Monitoring
- Data Storage & Management
- Networking
- Compliance & Security
Management Components & Dashboard: Cloud management includes:
- Self-service portals
- Resource monitoring
- Billing & chargeback models
- Automated orchestration dashboards
Business Intelligence Analytics: BI tools integrated with cloud reference architectures include:
- Big Data Analysis
- Predictive Analytics
- AI-driven Forecasting
6. Team Skills Requirements: A successful cloud architecture team requires:
- Cloud Solution Architects – Designing cloud strategies.
- DevOps Engineers – Managing cloud infrastructure automation.
- Cloud Security Analysts – Ensuring compliance.
- Data Scientists – Working with cloud-based analytics.
- AI & ML Specialists – Integrating AI for automation.
7. Concurrent Training Requirements: To maintain cloud proficiency, organizations must focus on:
- Certifications (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Security Compliance Training
- DevOps & Automation Training
- AI-Cloud Integration Courses
8. AI Integration for Future Interoperability: Cloud computing is rapidly evolving with AI-driven automation:
- AI-powered workload optimization (Dynamic scaling)
- AI-enhanced security models (Threat detection & response)
- AI-assisted cloud orchestration (Self-healing infrastructure)
- AI-driven business analytics (Predictive modeling)
Integration with AI and machine learning ensures autonomous cloud management, improved efficiency, and enhanced interoperability for future-ready enterprises. AI integration in cloud computing is an evolving frontier that enhances automation, security, scalability, and interoperability. Here’s a deeper dive:

Image Source: https://k21academy.com/ai-ml/the-role-of-ai-and-ml-in-cloud-computing/
1. AI-Powered Workload Optimization: AI-driven intelligent resource management allows dynamic scaling, predictive provisioning, and cost optimization. Key techniques include:
- Auto-scaling AI models – Adjusting compute power dynamically based on demand.
- Energy-efficient workload placement – AI-driven orchestration selects the most efficient cloud regions and resources.
- Predictive analytics for demand forecasting – AI predicts spikes and ensures seamless performance.
2. AI-Enhanced Security Models: With the growing threat landscape, AI is revolutionizing cloud security through:
- Real-time anomaly detection – AI identifies patterns and flags security threats.
- Automated risk assessment – Continuous AI monitoring evaluates vulnerabilities.
- Zero-trust architectures – AI enforces strict access control based on behavioral analytics.
3. AI-Assisted Cloud Orchestration: AI enables self-healing cloud infrastructures by:
- Automated troubleshooting – AI diagnoses and resolves system errors before failure.
- Policy-driven cloud governance – AI ensures compliance with regulatory frameworks.
- Multi-cloud orchestration – AI harmonizes workloads across different cloud providers.
4. AI-Driven Business Intelligence Analytics: AI enhances cloud-based data analytics with:
- Cognitive computing models – AI makes sense of unstructured data for business insights.
- Personalized user experiences – AI adapts cloud applications based on behavioral data.
- AI-assisted decision-making – AI predicts market trends using advanced analytics.
5. Future Interoperability Possibilities: The fusion of AI and cloud computing is shaping next-generation architectures, including:
- Federated AI for multi-cloud collaboration – Unified AI models across diverse cloud platforms.
- Quantum AI-driven cloud processing – Harnessing quantum computing for ultra-fast cloud computations.
- AI-powered decentralized cloud networks – Edge AI enables highly distributed computing.
How does AI improve security in cloud environments? AI plays a crucial role in strengthening cloud security by offering real-time threat detection, automated response, predictive risk analysis, and adaptive security measures. Here’s how AI enhances security in cloud environments:

Image Source: https://www.zucisystems.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-in-cloud-computing/
1. AI-Powered Threat Detection: AI enhances security by continuously monitoring cloud environments for anomalies:
- Behavioral Analytics – AI detects suspicious user behavior by analyzing login patterns and unusual activity.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) – AI-powered IDS identify threats by recognizing malicious network traffic.
- Fraud Detection Models – AI prevents fraud using machine learning models trained on historical attack patterns.
2. Automated Security Response & Self-Healing Systems: AI enables autonomous threat mitigation, reducing human intervention:
- Automated Incident Response – AI takes corrective actions like isolating infected systems in real time.
- Self-Healing Security Systems – AI applies automatic patches and restores configurations after cyberattacks.
- Threat Intelligence Integration – AI continuously learns from security incidents to improve future defense mechanisms.
3. Predictive Risk Analysis & Proactive Defense: AI anticipates and prevents potential cyber threats before they occur:
- Threat Forecasting – AI uses predictive analytics to foresee cyberattacks based on trends.
- Vulnerability Management – AI scans cloud environments for weaknesses and recommends fixes.
- Zero-Day Attack Detection – AI detects previously unknown threats by identifying abnormal activity.
4. AI-Driven Access Control & Identity Management: AI strengthens authentication and authorization processes:
- Adaptive Access Control – AI adjusts security measures based on contextual risk levels.
- Biometric Authentication – AI enables secure access using facial recognition or fingerprints.
- Continuous User Monitoring – AI ensures dynamic access by analyzing ongoing user behavior.
5. AI-Augmented Security Compliance & Governance: AI simplifies compliance with security regulations and policies:
- Automated Compliance Audits – AI verifies adherence to standards like ISO 27001, GDPR, and NIST.
- Security Policy Enforcement – AI ensures enterprise-wide security protocols are followed.
- AI-Driven Data Encryption – AI enhances encryption techniques for secure cloud storage.
6. AI in Cloud-Based Cybersecurity Solutions: Cloud providers integrate AI-powered security tools:

Image Source: https://www.orangemantra.com/blog/how-ai-in-cybersecurity-reimagines-cyberthreat/
- Microsoft Sentinel (AI-driven security monitoring)
- Google Chronicle (Threat intelligence analysis)
- AWS GuardDuty (AI-based threat detection)
Future of AI in Cloud Security: AI will continue to evolve cloud security by enabling autonomous cybersecurity, AI-driven deception techniques (e.g., honeypots for cyber-attack diversion), and quantum-resistant cryptography to tackle emerging threats. Here’s a breakdown of AI-driven security models used by major cloud service providers:

1. Google Cloud AI Security: Google Cloud integrates AI-powered security through its Gemini in Security framework. This AI-driven approach enhances:

- Threat detection using AI to analyze malicious code.
- Automated security responses for real-time mitigation.
- AI-assisted security event analysis to reduce manual effort.
2. Microsoft AI Security for Multi-Cloud Environments: Microsoft focuses on AI security governance across multi-cloud environments. Key features include:

- AI-driven compliance monitoring to prevent data oversharing.
- AI-powered risk detection for emerging threats like indirect prompt injections.
- Granular access controls to mitigate unauthorized AI usage.
3. IBM AI-Driven Compliance & Cloud Security: IBM emphasizes AI-driven compliance to tackle cloud security challenges. Their AI security model includes:

- Automated security audits to detect misconfigurations.
- AI-enhanced encryption for secure cloud storage.
- Predictive security analytics to prevent cyber threats.
Implementation of CCRA in real world: implementing a Cloud Computing Reference Architecture (CCRA) in a real business requires a well-planned strategy that aligns with enterprise needs, security requirements, and scalability. Here’s how businesses can implement CCRA effectively and the challenges they may face:
1. Define Business Goals & Cloud Strategy
- Identify core business needs that cloud services will support.
- Determine which cloud deployment models (Public, Private, Hybrid) best fit the organization’s structure.
- Choose the right service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) based on business objectives.
2. Select Cloud Providers & Technologies
- Evaluate enterprise cloud platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Assess network infrastructure to ensure seamless cloud adoption.
- Integrate AI-driven automation for workload optimization and security.
3. Establish Governance & Security Framework
- Implement identity and access management (IAM) to control cloud access.
- Define compliance policies aligned with industry standards (ISO 27001, NIST, GDPR).
- Deploy AI-based security solutions for threat detection and prevention.
4. Develop Cloud-Oriented Teams
- Train employees on cloud technologies.
- Hire cloud architects, DevOps engineers, and AI specialists.
- Establish cross-functional teams to manage cloud deployments.
5. Automate Operations & Optimize Costs
- Utilize cloud orchestration tools like Kubernetes and Terraform for scalability.
- Implement cost-optimization strategies to maximize cloud ROI.
- Introduce AI analytics dashboards for monitoring business performance.
6. Ensure Future Scalability & AI Integration
- Design cloud architecture for future AI-driven interoperability.
- Enable multi-cloud strategies for flexibility across different vendors.
- Leverage AI-powered analytics for smart decision-making.
Challenges in Implementing Cloud Computing Reference Architecture
1. Security & Compliance Risks
- Ensuring data privacy and meeting compliance standards can be complex.
- Implementing zero-trust security models is necessary but requires expertise.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
- Migrating legacy applications into cloud environments can be costly and time-consuming.
- Requires API-based integrations to connect on-premise systems with cloud services.
3. Skill Gaps & Workforce Challenges
- Finding qualified cloud professionals with expertise in DevOps, security, and AI.
- Continuous training is needed for evolving cloud technologies.
4. Managing Cost & ROI
- Unoptimized cloud resources can lead to unexpected high costs.
- Requires effective cloud cost management tools and strategies.
5. AI & Cloud Interoperability
- AI-driven cloud solutions require advanced algorithms and automation.
- Challenges in standardizing AI and cloud interactions across multi-cloud environments.
Future Considerations: by overcoming these challenges with structured governance, AI-driven automation, and skill development, businesses can effectively implement Cloud Computing Reference Architecture to maximize scalability, security, and efficiency.
Here are some real-world case studies showcasing successful implementations of Cloud Computing Reference Architecture:
1. Netflix – Scaling with AWS
Netflix migrated its entire infrastructure to Amazon Web Services (AWS) to handle massive global traffic. The cloud transition resulted in:
- 30% reduction in operational costs.
- Seamless scalability to support over 200 million subscribers.
- Improved content delivery with minimal latency.
2. Airbnb – Handling Seasonal Peaks
Airbnb adopted AWS cloud infrastructure to manage fluctuating demand. Their cloud strategy included:
- Microservices architecture for independent scaling.
- Dynamic resource allocation during peak seasons.
- Enhanced user experience with faster booking processes.
3. Target – Cloud-First Strategy
Target implemented a hybrid cloud model to modernize its retail operations. The benefits included:
- 30% increase in online sales year-over-year.
- Rapid application deployment within hours.
- Improved customer engagement through AI-driven analytics.
4. Healthcare Provider – Cloud-Based Patient Management
A leading healthcare provider leveraged cloud computing to streamline patient data management:
- 25% decrease in patient processing times.
- Enhanced data accessibility for medical professionals.
- Improved patient satisfaction metrics.
5. Major Bank – AI-Driven Cloud Security
A financial institution adopted cloud-based AI security models, leading to:
- 50% increase in transaction speed.
- 60% reduction in fraud incidents.
- 35% rise in active mobile users within six months.
The most prominent vendors for Public Cloud Services in 2025 include:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Market leader with 175+ cloud services.
- Strong presence in AI, machine learning, and multi-cloud solutions.
- Offers serverless computing, storage, and networking.
2. Microsoft Azure
- Enterprise-focused cloud solutions with deep AI integration.
- Hybrid cloud capabilities with Azure Arc.
- Security-first approach with Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- AI-driven cloud services with Gemini AI.
- Data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
- Multi-cloud interoperability with Anthos.
4. IBM Cloud
- AI-powered security and compliance solutions.
- Hybrid cloud and quantum computing integration.
- Enterprise-grade cloud services for regulated industries.
5. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- High-performance cloud computing for databases.
- AI-enhanced automation for enterprise workloads.
- Multi-cloud compatibility with Azure and AWS.
6. Alibaba Cloud
- Asia’s leading cloud provider with global expansion.
- AI-driven cloud security and big data analytics.
- Strong presence in e-commerce and fintech.
7. Salesforce Hyperforce
- Cloud-native CRM with AI-powered automation.
- Multi-cloud architecture for scalability.
- Industry-specific cloud solutions.
Several cloud vendors have built custom OpenStack-based solutions to provide scalable, flexible, and open-source cloud services. Here are some of the most prominent ones:
1. Rackspace
- One of the founding members of OpenStack.
- Offers managed OpenStack services for enterprises.
- Provides multi-cloud solutions with OpenStack integration.
2. Red Hat OpenStack Platform
- Enterprise-grade OpenStack distribution.
- Deep integration with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
- Focuses on hybrid cloud and Kubernetes orchestration.
3. OVH Cloud
- European cloud provider using OpenStack for public cloud services.
- Operates multi-region OpenStack deployments.
- Offers high-performance computing (HPC) and AI workloads.
4. Open Telekom Cloud (Deutsche Telekom)
- GDPR-compliant OpenStack cloud for European businesses.
- Provides secure and scalable cloud solutions.
- Focuses on data sovereignty and privacy.
5. IBM Cloud
- Uses OpenStack for private cloud solutions.
- Offers AI-driven automation and hybrid cloud capabilities.
- Provides enterprise-grade security and compliance.
6. Mirantis OpenStack
- Fully managed OpenStack cloud for enterprises.
- Focuses on containerized workloads with Kubernetes.
- Provides multi-cloud interoperability.
7. Fuga Cloud
- Netherlands-based OpenStack provider.
- Offers developer-friendly OpenStack APIs.
- Provides customized cloud solutions for businesses.
These vendors leverage custom OpenStack implementations to provide scalable, secure, and open-source cloud services to the big players who wants to provide Public Cloud Services to their locale.