 Reading Time: 3 minutes
Reading Time: 3 minutes

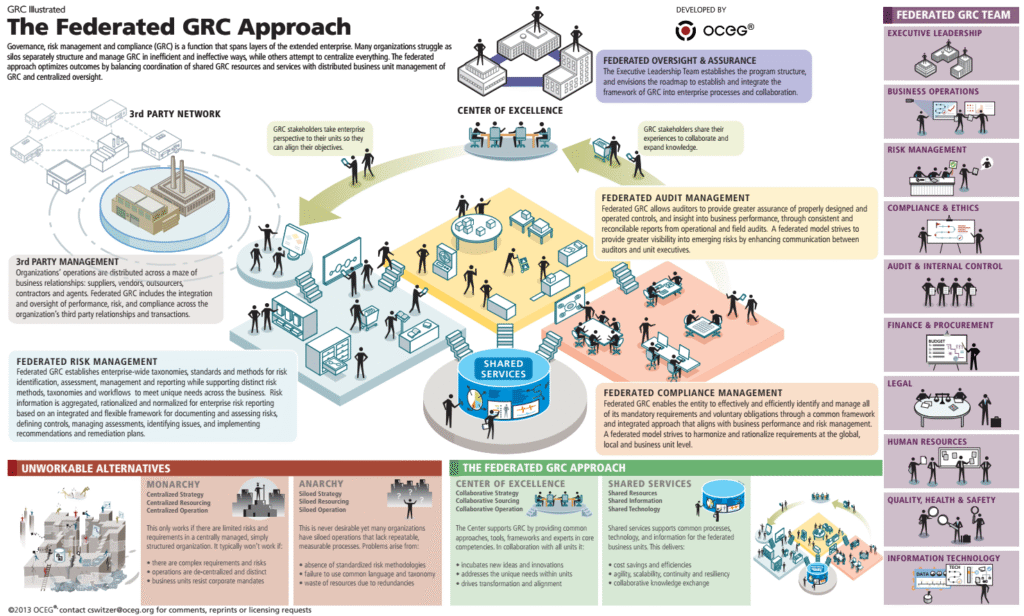
Image source: OCEG
Organizations face unprecedented challenges in governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC). The increasing complexity of risks, regulations, and operational demands necessitates a modern, integrated approach to GRC. To connect the dots between risks, compliance, and other GRC elements that impact business performance, organizations need an integrated data model that aggregates distributed and disconnected information from across business silos, ties them together, and enables stakeholders to analyze this data from various perspectives. Achieving this requires a mature GRC management capability that combines a coordinated strategy and processes on a next-generation GRC information and technology architecture, delivering 360° contextual awareness and clarity into risk and controls while ensuring compliance in a dynamic business environment.
Key components of integrated GRC architecture:
An integrated Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) architecture combines three foundational components to ensure effective organizational operation, efficient risk management, and adherence to regulations. Here are the key components:
- Governance:
- Establishes decision-making structures, policies, and processes.
- Defines roles and responsibilities for oversight and accountability.
- Ensures alignment with strategic objectives and ethical standards.
- Risk Management:
- Identifies, assesses, and prioritizes risks across the organization.
- Implements controls to mitigate risks.
- Monitors risk exposure and adjusts strategies as needed.
- Compliance:
- Ensures adherence to laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Develops policies, procedures, and controls.
- Regularly assesses compliance and addresses any gaps.
How to implement integrated GRC architecture:
Implementing integrated Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) architecture involves several steps:
- Assessment and Strategy:
- Evaluate existing GRC processes, tools, and data sources.
- Define the organization’s GRC strategy, objectives, and priorities.
- Data Integration and Centralization:
- Identify relevant data sources (e.g., risk registers, compliance reports).
- Integrate data into a centralized GRC platform or repository.
- Unified Framework:
- Develop a common framework for risk assessment, control evaluation, and compliance monitoring.
- Align risk and compliance activities with business objectives.
- Technology Infrastructure:
- Invest in GRC software solutions that support integration.
- Ensure interoperability between existing systems (e.g., ERP, CRM).
- Process Harmonization:
- Streamline GRC processes across departments.
- Standardize risk assessment methodologies and compliance workflows.
- Stakeholder Engagement:
- Involve key stakeholders (executives, legal, IT, etc.) in GRC initiatives.
- Foster collaboration and communication.
- Training and Awareness:
- Educate employees on GRC principles, policies, and procedures.
- Promote a culture of risk awareness and compliance.
How to measure the effectiveness of their GRC architecture:

Image source: OCEG
Measuring the effectiveness of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) architecture is crucial for organizations. Here are the key steps and metrics to consider:
- GRC Metrics:
- KPIs (Key Performance Indicators): These track overall progress and performance against compliance and risk targets.
- KRIs (Key Risk Indicators): Indicators that highlight potential risks.
- KCIs (Key Control Indicators): Metrics assessing control effectiveness.
- Design Effectiveness:
- Evaluate how logically the GRC system is designed to meet legal and other requirements.
- Assess whether it includes necessary elements to evaluate and address risks effectively.
- Operating Effectiveness:
- Measure how well the GRC system operates as intended.
- Monitor compliance performance, identify improvement areas, and demonstrate efforts to stakeholders.
This is just not a checklist where answers are limited to YES/NO, but each unique situation would prove to be an effective measuring technique.
How to align organizations GRC metrics with business objectives:
Aligning Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) metrics with business objectives is essential for effective decision-making. Here’s how organizations can do it:
- Strategic Mapping:
- Identify key business goals and strategic priorities.
- Map GRC metrics to these objectives. For example:
- If a business aims to expand into new markets, track compliance with international regulations.
- If profitability is a goal, monitor financial risk metrics.
- Risk-Return Balance:
- Evaluate risks in the context of business opportunities.
- Prioritize metrics that balance risk mitigation with growth potential.
- Customization:
- Tailor GRC metrics to specific business units or functions.
- Consider industry-specific requirements.
- Continuous Review:
- Regularly assess whether GRC metrics align with evolving business needs.
- Adjust as necessary to stay relevant.
Business alignment ensures GRC efforts contribute directly to organizational success!