 Reading Time: 2 minutes
Reading Time: 2 minutes
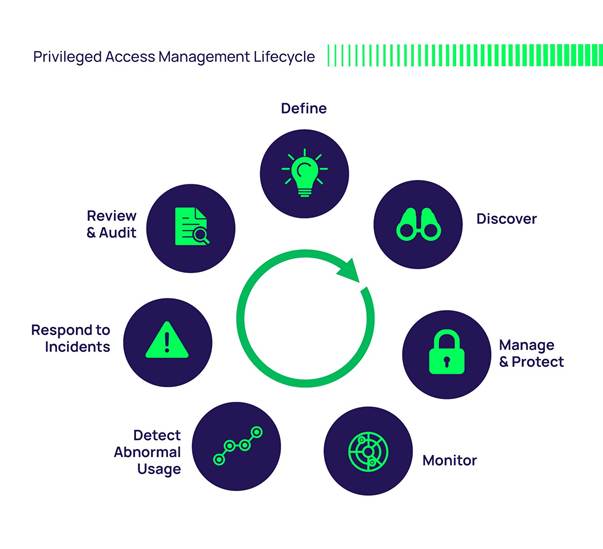
PAM organizes the key aspects of securing high-privilege accounts and activities. It typically includes core functionalities like discovery, control, password management, session monitoring, and compliance, along with components like account discovery, access management, and password vault. The mindmap helps understand how PAM systems work, from identifying privileged accounts to ensuring secure access, logging, and auditing.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of what a PAM mindmap might include:

Image Source: https://delinea.com/what-is/privileged-access-management-pam
Central Topic: Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Core Branches:
Identification and Discovery:
- Identifying all privileged accounts (user, application, system).
- Cataloging and understanding the roles and permissions associated with each account.
- Discovering privileged accounts in various systems, including on-premises, cloud, and OT environments.
Access Control:
- Implementing the principle of least privilege, granting only necessary access.
- Enforcing strong password policies and enforcing password rotation.
- Utilizing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced security.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) access, granting temporary elevated access only when needed.
Password Management:
- Centralized management of privileged credentials.
- Securely storing passwords in a password vault.
- Automated password rotation and lifecycle management.
Session Monitoring and Recording:
- Tracking and logging all activities during privileged sessions.
- Providing an audit trail for security investigations and compliance audits.
- Analyzing unusual privileged activity for potential security threats.
Compliance and Auditing:
- Generating reports on privileged access activities and potential security anomalies.
- Meeting compliance requirements for various regulations.
- Facilitating audits and investigations related to privileged access.
Components of a PAM Solution:
- Access Manager: Manages access to privileged accounts and roles.
- Password Vault: Securely stores and manages privileged credentials.
- Session Manager: Monitors and records activities during privileged sessions.
- Universal Tunneling: Enables secure communication across OT infrastructure.
Optional Branches (depending on complexity):
- User Roles and Permissions:
- Defining roles based on job functions and responsibilities.
- Assigning privileges based on roles and permissions.
Integration with Other Tools:
- Integrating with existing security and IT management tools.
- Integrating with identity and access management (IAM) systems.
Threat Detection and Prevention:
- Analyzing privileged activity for suspicious patterns.
- Implementing security controls to prevent unauthorized access.

Image Source: https://delinea.com/what-is/privileged-access-management-pam