 Reading Time: 5 minutes
Reading Time: 5 minutes

Image Source: What is OAuth? (An Introduction to OAuth and OpenID) – The Genius Blog
OAuth 2.0 is a widely used authorization framework that enables secure access to resources without exposing user credentials. Here’s a breakdown of its architecture, possibilities of integration, and deployment challenges.
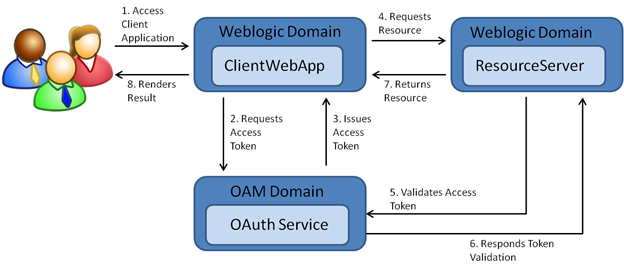
Image Source: OAuth 2.0
OAuth Architecture: OAuth 2.0 consists of several key components:
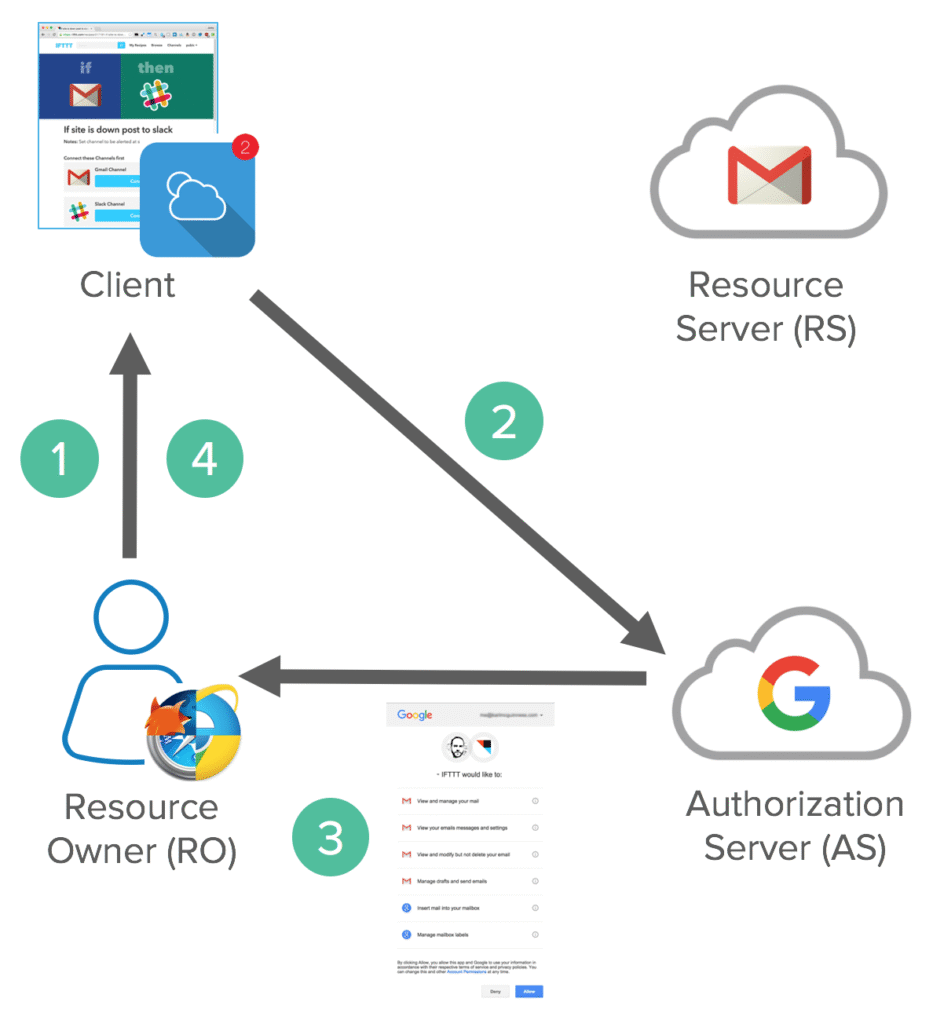
Image Source: What the Heck is OAuth? | Okta Developer
- Resource Owner: The user who grants access to their data.
- Client: The application requesting access.
- Authorization Server: Issues access tokens after authentication.
- Resource Server: Hosts the protected resources and validates access tokens.
A typical OAuth flow involves:
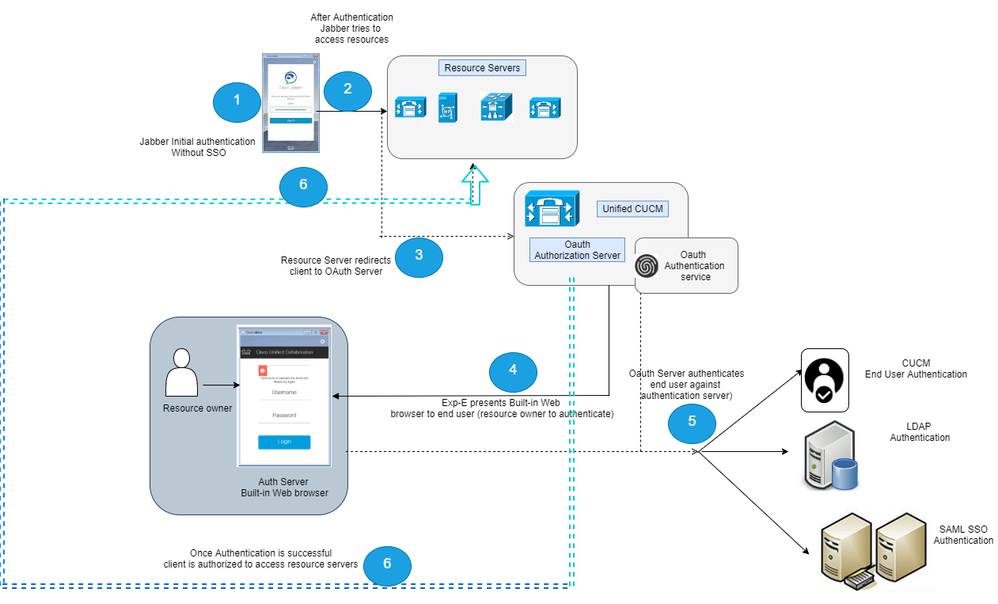
Image Source: Understanding OAuth and MRA – Cisco Community
- The client requests authorization from the resource owner.
- The authorization server issues an authorization code.
- The client exchanges the code for an access token.
- The client uses the token to access the resource server.
Integration Possibilities: OAuth can be integrated into various applications, including:
- Web Applications: Enables Single Sign-On (SSO) and secure API access.
- Mobile Apps: Uses authorization flows like PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) for enhanced security.
- Microservices: Helps manage authentication across distributed systems.
- IoT Devices: Ensures secure communication between connected devices.
Deployment Challenges: While OAuth is powerful, deploying it comes with challenges:
- Security Risks: Token leakage, improper storage, and weak authentication mechanisms can lead to vulnerabilities.
- Complexity: Implementing OAuth requires careful configuration of authorization flows and token management.
- Scalability: Handling large-scale authentication requests efficiently can be challenging.
- Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility across different platforms and identity providers.
Tools that are commonly used for OAuth integration: There are several tools available for OAuth integration, depending on your needs. Here are some commonly used ones:
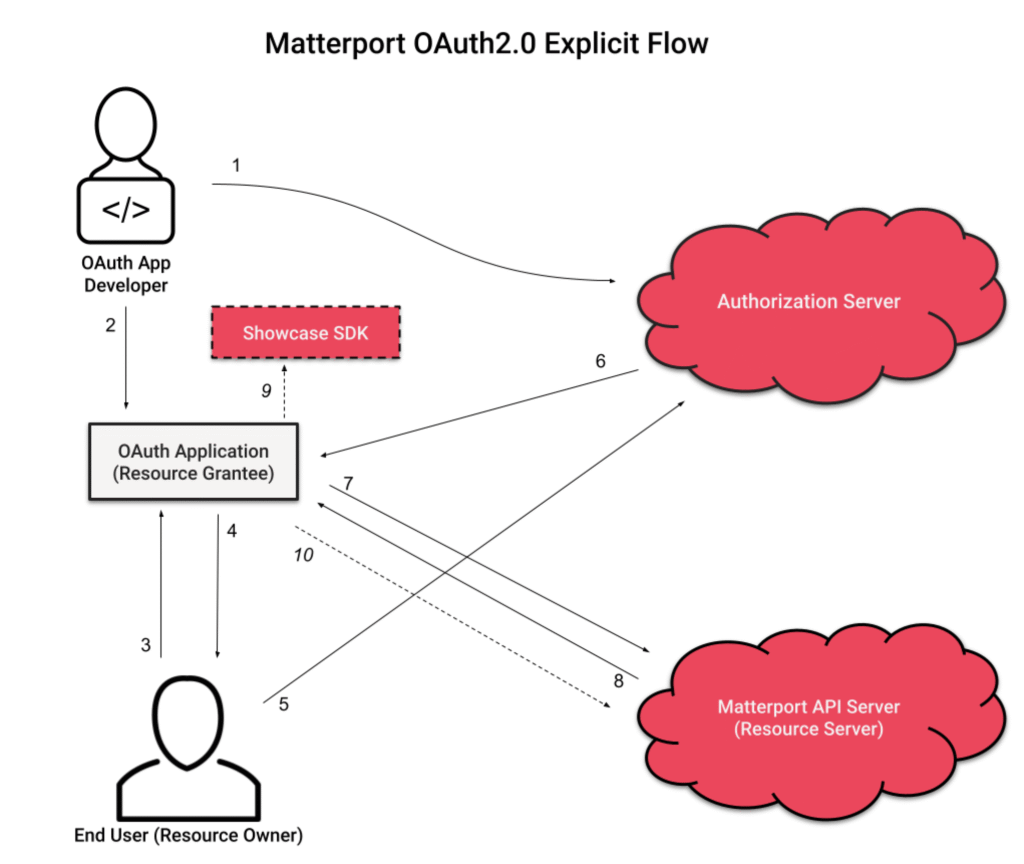
Image Source: OAuth Integration: For Application Developers
OAuth Servers
- Keycloak: An open-source identity and access management solution.
- Auth0: A cloud-based authentication and authorization service.
- IdentityServer: A .NET-based framework for implementing OAuth and OpenID Connect.
OAuth Libraries
- simple-oauth2 (JavaScript): A lightweight OAuth 2.0 client library.
- Authlib (Python): A comprehensive OAuth and OpenID Connect library.
- Spring Security OAuth (Java): A powerful framework for securing applications.
Testing & Debugging Tools
- Postman: Helps test OAuth flows and API authentication.
- OAuth.com Playground: A tool for experimenting with OAuth requests.
Best practices for using OAuth in projects: Using OAuth securely and efficiently requires following best practices to ensure authentication and authorization are handled properly. Here are some key recommendations:
Security Best Practices
- Use PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange): This prevents authorization code interception attacks, especially in mobile and single-page applications.
- Avoid Implicit Grant Flow: The implicit grant flow is considered insecure due to token exposure in URLs.
- Secure Token Storage: Store access and refresh tokens securely using encrypted storage mechanisms.
- Validate Redirect URIs: Ensure that redirect URIs are pre-registered and strictly validated to prevent open redirect vulnerabilities.
- Limit Token Scope: Request only the minimum necessary permissions to reduce security risks.
Implementation Best Practices
- Use Incremental Authorization: Request permissions only when needed rather than all at once.
- Handle Token Expiration Gracefully: Implement automatic token refresh mechanisms to maintain session continuity.
- Monitor and Revoke Tokens: Regularly audit token usage and revoke unused or compromised tokens.
- Use Strong Client Authentication: Ensure that client applications authenticate securely using client secrets or mutual TLS.
Example of OAuth implementation: A simple example of OAuth 2.0 implementation using the Authorization Code Flow, which is commonly used for web applications.
Step-by-Step OAuth Implementation
1. Register Your Application
- Sign up with an OAuth provider (e.g., Google, GitHub, or Auth0).
- Register your application to obtain Client ID and Client Secret.
- Define Redirect URIs where the provider will send authorization responses.
2. Request Authorization
- Redirect users to the OAuth provider’s authorization endpoint:
“`
https://oauth-provider.com/auth?client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URI&response_type=code&scope=read_profile
“`
- The user logs in and grants permission.
3. Exchange Authorization Code for Access Token
- Your backend sends a request to the OAuth provider:
“`
POST https://oauth-provider.com/token
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID
client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET
code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE
redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URI
grant_type=authorization_code
“`
- The provider responds with an access token.
4. Access Protected Resources
– Use the access token to make API requests:
“`
GET https://oauth-provider.com/userinfo
Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN
“`
- The provider returns user data.
Example Implementations
Sample code for OAuth in Node.js
A basic example of implementing OAuth 2.0 in Node.js using Express and the `simple-oauth2` library.
Step-by-Step OAuth Implementation in Node.js
1. Install Dependencies
- Run the following command to install required packages:
“`bash
npm install express simple-oauth2 dotenv
“`
2. Set Up Environment Variables
Create a `.env` file to store your OAuth credentials:
“`
CLIENT_ID=your_client_id
CLIENT_SECRET=your_client_secret
AUTHORIZATION_URL=https://provider.com/oauth/authorize
TOKEN_URL=https://provider.com/oauth/token
REDIRECT_URI=http://localhost:3000/callback
“`
3. Create an Express Server
javascript
require(‘dotenv’).config();
const express = require(‘express’);
const { AuthorizationCode } = require(‘simple-oauth2’);
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
const oauth2 = new AuthorizationCode({
client: {
id: process.env.CLIENT_ID,
secret: process.env.CLIENT_SECRET,
},
auth: {
tokenHost: process.env.TOKEN_URL,
authorizePath: process.env.AUTHORIZATION_URL,
},
});
app.get(‘/auth’, (req, res) => {
const authorizationUri = oauth2.authorizeURL({
redirect_uri: process.env.REDIRECT_URI,
scope: ‘profile email’,
});
res.redirect(authorizationUri);
});
app.get(‘/callback’, async (req, res) => {
const { code } = req.query;
const tokenParams = {
code,
redirect_uri: process.env.REDIRECT_URI,
};
try {
const accessToken = await oauth2.getToken(tokenParams);
res.json(accessToken.token);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: ‘Token exchange failed’ });
}
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Resources for Further Learning
– A detailed guide on implementing OAuth. [OAuth 2.0 in Node.js]: https://blog.logrocket.com/implement-oauth-2-0-node-js/
– How to set up an OAuth server in Node.js. [OAuth Server with Express](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/implementing-an-oauth-server-with-nodejs-and-express/):
– A practical example of OAuth integration. [OAuth 2.0 with Node.js](https://www.sohamkamani.com/nodejs/oauth/):
– You can find a detailed architecture diagram[here] https://bing.com/search?q=oauth+architecture+diagram+integration+deployment
– For a deeper dive into OAuth deployment strategies, you can check out [this guide] https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/architecture/deployment-external-authentication-access-control or
– Explore how Keycloak can be used for OAuth authorization [here]: https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/oauth-20-authentication-keycloak
– For a deeper dive into OAuth tools, you can check out [this guide] (https://blog.dreamfactory.com/implementing-oauth-2.0-in-rest-apis-complete-guide).
– A detailed walkthrough of OAuth implementation. [OAuth 2.0 Guide] (https://infisical.com/blog/guide-to-implementing-oauth2):
– How to integrate OAuth with Spring Boot. [Spring Security OAuth] (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/implementing-oauth2-with-spring-security-a-step-by-step-guide/):
– Implementing OAuth in enterprise applications.: [Jakarta EE OAuth] (https://www.baeldung.com/java-ee-oauth2-implementation):
– For a deeper dive into OAuth best practices, you can check out [this guide] (https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/resources/best-practices) or
– Explore security recommendations from the OAuth community [here] (https://oauth.net/2/oauth-best-practice/).