Let’s delve into the world of endpoint security and explore the various solutions available to fortify your organization’s defenses.
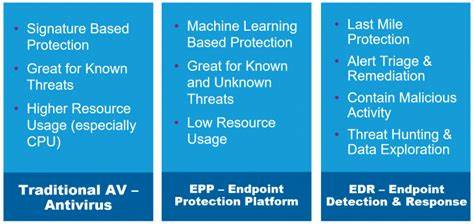
Image Courtesy: What is EDR? EDR vs. MDR vs. EPP Security – Critical Start
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):
- Focus: EDR revolves around monitoring and safeguarding individual endpoints (such as desktops, laptops, and smartphones) within your organization’s network.
- Functionality:
- Collects telemetry data from endpoints, providing real-time visibility into their activities.
- Detects and responds to anomalous behavior.
- Leverages behavioral analysis, signature-based detection, and machine learning to identify known and unknown threats.
- Limitation: EDR’s scope is limited to endpoints, which means it may not provide insights into threats occurring elsewhere in the network (e.g., email attacks).
- Recommendation: EDR is valuable for endpoint protection but should be complemented with other security layers.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR):
- Holistic Approach: XDR extends beyond endpoint protection to include multiple security layers, such as networks, email, cloud services, and endpoints.
- Unified View of Threats:
- Correlates information from different sources to improve threat detection and response.
- Provides a unified and correlated view of threats across the entire organization.
- Benefits:
- Reduces the time to detect and remediate threats.
- Seamlessly integrates with existing security tools and infrastructure.
- Consideration: XDR solutions may have higher costs and complexity compared to traditional EDR solutions.
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR):
- Outsourced Approach:
- MDR is not a standalone technology but rather a service offered by third-party cybersecurity providers.
- Ideal for organizations lacking internal resources or expertise in security operations.
- Coverage:
- MDR covers threat detection and response across various layers, including endpoints, networks, and more.
- Provides a fully managed and outsourced security solution.
- Advantages:
- Relieves the burden on internal teams.
- Offers expert monitoring and incident response.
- Outsourced Approach:
Consider a combination of EDR, XDR, and MDR to create a robust security posture that protects your endpoints, detects threats across multiple layers, and ensures timely responses. Do remember that each solution has its strengths and limitations, so tailor your approach based on your organization’s specific needs and risk profile, and lastly, all of its data needs to be fed into the SIEM & SOAR.
References:
- EDR vs MDR vs XDR: What’s the Difference? | StrongDM
- What is Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)? | IBM
- EDR, XDR & MDR: Which Detection & Response System Is Best? | Splunk
- What Is EDR? Endpoint Detection and Response | Microsoft Security
- Extending Security Beyond the Endpoint with Symantec XDR | Symantec Enterprise Blogs
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR) | Microsoft Security
- What is XDR? Extended Detection and Response Security (fortinet.com)
- Endpoint Security: EDR, XDR, and MDR Solutions | Flatiron School