 Reading Time: 3 minutes
Reading Time: 3 minutes
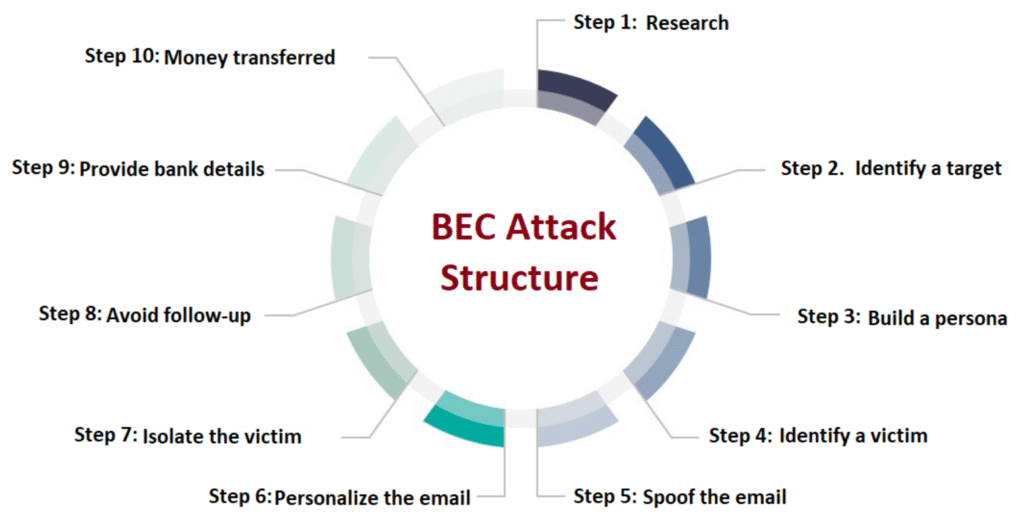
In a typical Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack, attackers impersonate trusted individuals or organizations to deceive employees into taking harmful actions like transferring funds or sharing sensitive information. This involves research, email manipulation, and often social engineering tactics to exploit trust and urgency.
Attack Methods:

Image Source: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/12/1/42
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
1. Research and Reconnaissance: Attackers gather information about the target organization, including key personnel, their communication patterns, and financial processes. This information helps them tailor their impersonation attempts and choose the most effective targets.
2. Email Spoofing or Compromise:
- Spoofing: Attackers create email addresses that closely resemble legitimate contacts, like executives or vendors, to appear trustworthy.
- Account Compromise: Attackers may gain access to legitimate email accounts, either through phishing or other methods, and use them to send fraudulent messages.
3. Email Manipulation: Attackers craft compelling emails that request urgent actions, like transferring funds, changing payment details, or sharing confidential data. They often use:
- Urgency: Phrases like “urgent,” “important,” or “quick” create a sense of pressure.
- Authority: Impersonating executives, CFOs, or other figures of authority.
- Specificity: Providing detailed instructions and justifications for the request to enhance legitimacy.
- Social Engineering: Exploiting the victim’s trust and fear of appearing hesitant.
4. Fraud Execution: If the victim falls for the scam, they take the requested action, such as transferring funds to a fraudulent account or sharing sensitive information.
5. Monetization and Cover-up: Attackers quickly move stolen funds to offshore accounts or convert them to cryptocurrency, making it difficult to trace. They may also attempt to delete evidence of the attack and continue manipulating the victim for extended periods.
6. Extraction: After successfully obtaining the desired information or funds, attackers may withdraw them or use the information for further attacks, according to NinjaOne.
Dangers could result from a successful BEC attack
A successful Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack can lead to significant financial losses, data theft, and potential reputational damage for the organization. BEC attacks often target executives, finance personnel, and IT staff, tricking them into divulging sensitive information, transferring funds to fraudulent accounts, or installing malware.
Here’s a more detailed look at the dangers:
Financial Losses:
- BEC attacks can result in the unauthorized transfer of large sums of money from company accounts to attacker-controlled accounts.
- This can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, potentially bankrupting smaller businesses.
- The cost of a BEC breach can be in the millions, according to IBM’s report.
Data Theft and Privacy Violations:
- Attackers may steal sensitive information such as customer data, intellectual property, and employee personal information.
This stolen data can be used in further attacks, sold on the dark web, or used for blackmail. Data breaches can lead to lawsuits, fines, and a loss of customer trust.
Reputational Damage:
- A successful BEC attack can damage a company’s reputation and erode customer trust.
- News of a major data breach or financial loss can be widely publicized, negatively impacting the organization’s image.
Additional Risks:
- Ransomware: BEC attacks can be used to deliver ransomware, locking down company systems and demanding payment for their release.
- Employee Exposure: BEC attacks can lead to employees being targeted with other types of cyberattacks, such as phishing or malware campaigns.
- Third-Party Impact: If a BEC attack compromises a company’s relationships with third-party vendors or partners, it can lead to disruptions in operations and financial losses.
Remediation:
- Make sure your DMARC, DKIM & SPF configuration is in place.
- Keep an eye out for a Cyrillic character in a spoofed email.
- User training and understanding on high value employees is a must.
Email protection: involves several practices to enhance security:
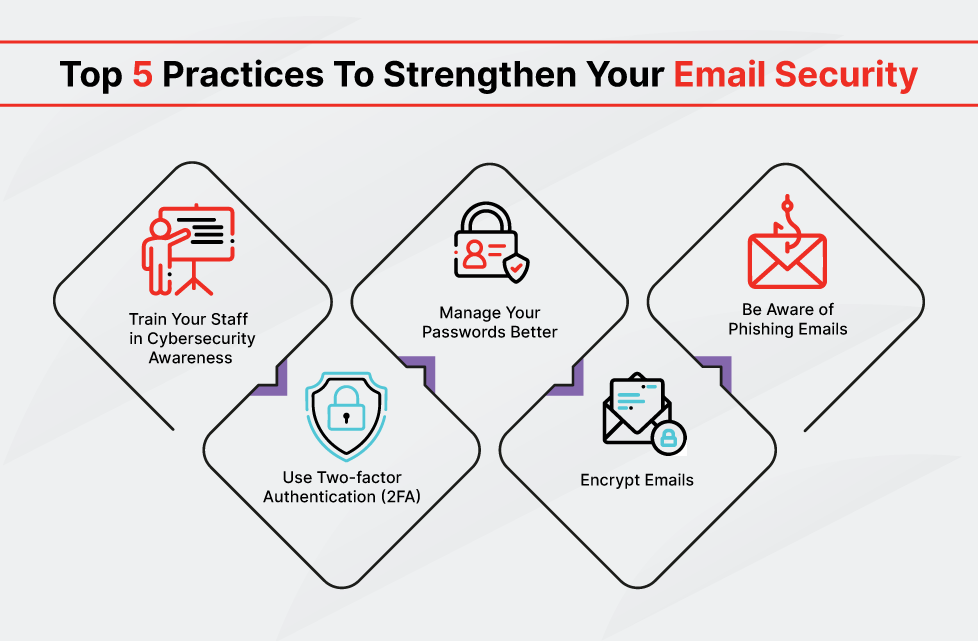
Image source: https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/email-security-best-practices
- Preventing email-based cyber attacks: This includes stopping phishing attacks, blocking malware delivery, and filtering spam.
- Using antivirus protection: Install antivirus software to protect against malware.
- Secure habits: Regularly check login activity, avoid public Wi-Fi, and delete unused accounts.
- Implementing 2-factor authentication: Enhance security by requiring an additional verification step.
- Encrypting emails: Protect the contents of emails from unauthorized access.
Further Reading: Selecting your email security product
Gartner Peer Insights Review: Best Email Security Platforms Reviews 2025 | Gartner Peer Insights