 Reading Time: 2 minutes
Reading Time: 2 minutes
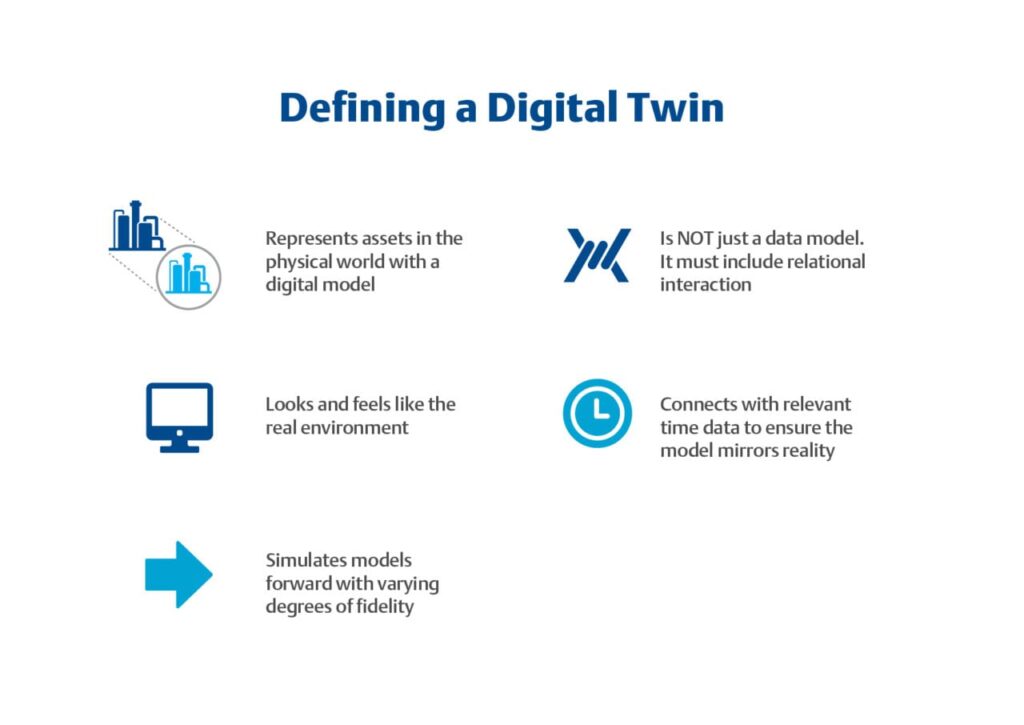
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a real-world object, system, or process, designed to accurately reflect its physical counterpart. It uses real-time data from sensors and other sources to create a dynamic, constantly updating model that mirrors the physical entity. This allows for analysis, simulation, and prediction of behavior, enabling better decision-making and optimization in various applications.

Image Source: Understanding the Digital Twin – Chemical Engineering | Page 1
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Core Concepts:
- Virtual Representation: A digital twin is a software-based model, a digital “twin” of a physical entity.
- Real-time Data: It continuously receives data from the real-world object, allowing it to evolve and reflect changes in the physical world.
- Dynamic Simulation: Digital twins can be used to simulate various scenarios and predict the behavior of the physical object under different conditions.
- Decision-Making Support: By analyzing the digital twin’s behavior, users can make informed decisions about the physical object’s operation, maintenance, and even design.
How it Works:
- Data Acquisition: Sensors, IoT devices, and other sources collect data about the physical object’s state, performance, and environment.
- Data Integration: This data is fed into the digital twin model, updating it in real-time.
- Analysis and Simulation: Users can analyze the data, run simulations, and test different scenarios using the digital twin.
- Decision Making: Based on the insights gained from the digital twin, users can optimize the physical object’s performance, predict potential issues, and make informed decisions.
Applications:
- Manufacturing: Optimizing production processes, predicting equipment failures, and improving product design.
- Healthcare: Simulating patient physiology, developing personalized treatment plans, and optimizing hospital operations.
- Infrastructure: Monitoring the health of bridges, tunnels, and other critical infrastructure, predicting maintenance needs, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Energy: Optimizing energy consumption, predicting equipment failures in power plants, and improving grid management.
- Cities: Simulating traffic flow, optimizing resource management, and improving urban planning.
Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: Digital twins can help optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Performance: By simulating and analyzing different scenarios, digital twins can help optimize the performance of physical objects and systems.
- Reduced Downtime: Predicting potential failures and optimizing maintenance schedules can minimize downtime and improve the reliability of physical assets.
- Informed Decision Making: Digital twins provide a powerful tool for data-driven decision making, leading to better outcomes.
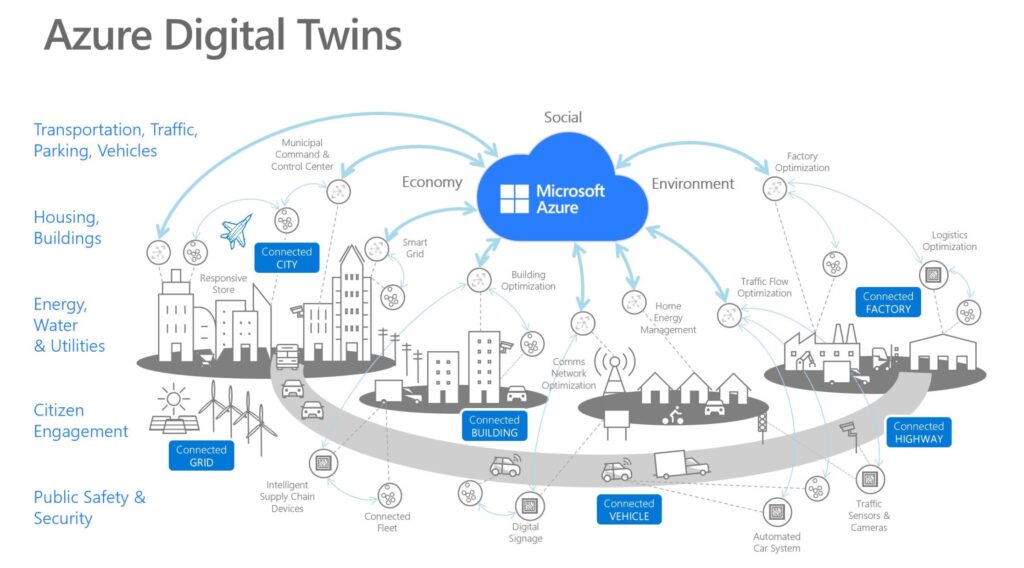
AZURE Digital Twin
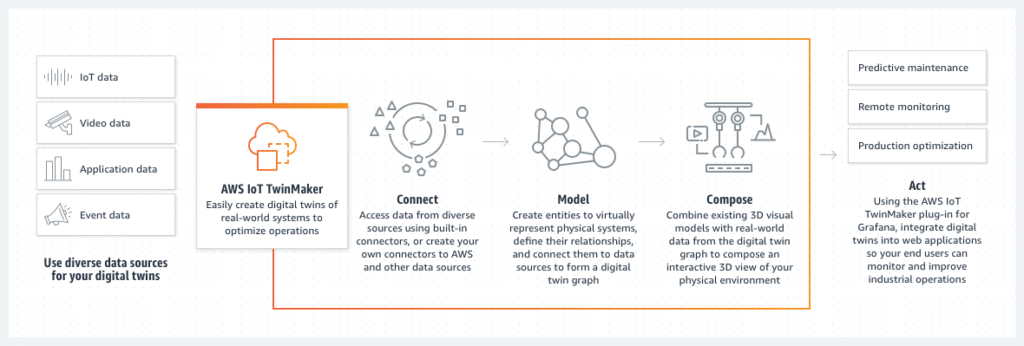
AWS Digital Twin
Read More: