 Reading Time: 4 minutes
Reading Time: 4 minutes

Status: Final Blueprint
Author: Shahab Al Yamin Chawdhury
Organization: Principal Architect & Consultant Group
Research Date: April 9, 2023
Location: Dhaka, Bangladesh
Version: 1.0 (Summary)
Executive Blueprint: The Future-Fit I&O Organization
The role of Infrastructure & Operations (I&O) has transformed from a back-office cost center to a strategic business enabler that powers digital innovation and competitive advantage. Modern I&O is an integrated ecosystem of cloud, edge, and on-premises systems aligned with business value streams. This playbook provides a blueprint for this transformation, built on four foundational pillars:
- Agility: The capacity to respond rapidly to changing business needs through modular architectures and automation.
- Resilience: The ability to anticipate, withstand, and recover from disruptions, secured through robust design and governance.
- Efficiency: The optimization of costs, resources, and processes through practices like FinOps and automation.
- Innovation: Acting as a catalyst for deploying disruptive technologies like AI by providing stable, scalable platforms.
Part 1: Foundational Strategy and Governance
Chapter 1: Establishing the Governance Framework
A modern I&O organization requires a hybrid governance model that integrates established frameworks with agile principles to balance control, efficiency, and speed.
- Hybrid Governance Model:
- COBIT 2019 (The “Why”): Provides the overarching governance framework, aligning I&O activities with enterprise goals and risk appetite.
- ITIL 4 (The “How”): Offers the practical blueprint for IT service management (ITSM), detailing how to deliver value through the Service Value System (SVS).
- DevOps (The “How Fast”): A cultural philosophy that accelerates delivery through collaboration, shared responsibility, and end-to-end automation.
- Alignment: The COBIT Goals Cascade translates high-level stakeholder needs into specific, actionable I&O objectives, ensuring work is purposefully directed at delivering business value.
Chapter 2 & 3: Design for Resilience, Risk, and Compliance
Infrastructure must be architected for resilience and security from the ground up, guided by a structured approach to risk management.
- Core Architectural Principles:
- Redundancy & Fault Tolerance: Duplicate components to ensure continuity if a primary one fails.
- Isolation & Containment: Use modular designs (e.g., microservices) to limit the “blast radius” of a failure.
- Self-Healing & Automated Recovery: Build systems that recover from failures with minimal human intervention.
- Security by Design: Embed security using frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) for risk management and ISO 27001 for selecting specific security controls.
- Risk Management: Implement the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF), a seven-step process (Prepare, Categorize, Select, Implement, Assess, Authorize, Monitor) for managing risk throughout the system lifecycle. Maintain a central Risk Register to track threats, likelihood, impact, and mitigation plans.
Part 2: The Modern Operating Model
Chapter 4 & 5: Structuring for Agility and Defining Roles
Modern I&O requires organizational structures that break down silos and align teams with business outcomes.
- Platform Engineering: Treat infrastructure as a product by creating an Internal Developer Platform (IDP). A central platform team builds and maintains a curated, self-service platform that reduces cognitive load for developers and accelerates delivery.
- Site Reliability Engineering (SRE): A discipline that treats operations as a software engineering problem. SRE is built on:
- Service Level Objectives (SLOs): Quantitative reliability targets.
- Error Budgets: The acceptable level of unreliability. If the budget is spent, all new feature releases are frozen to focus on stability.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Utilize RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) matrices to clarify roles for critical processes. Key modern roles include Platform Engineer, SRE, Cloud Infrastructure Engineer, and FinOps Analyst.
Chapter 6: Financial Governance (FinOps)
FinOps is the operating model for cloud financial management, bringing together finance, tech, and business teams to make data-driven spending decisions. It operates on a continuous cycle:
- Inform: Gain visibility into cloud spending.
- Optimize: Eliminate waste and leverage discounts.
- Operate: Embed cost as a key metric in daily operations.
Part 3: Operational Execution and Excellence
Chapter 7: The Automated Infrastructure Lifecycle
Automation is the core mechanism for achieving speed, consistency, and reliability at scale.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): The cornerstone of modern operations. Manage and provision infrastructure through machine-readable code (e.g., Terraform, Ansible), enabling version control, consistency, and speed.
- CI/CD for Infrastructure: Apply Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery pipelines to automate the testing and deployment of infrastructure changes.
Chapter 8 & 9: Observability and World-Class Support
- Full-Stack Observability: Evolve from reactive monitoring to proactive observability. An observable system is one whose internal state can be understood from its external outputs—the “three pillars”:
- Metrics: Numeric, time-series data (e.g., CPU utilization).
- Logs: Timestamped records of discrete events.
- Traces: End-to-end journey of a request through a distributed system.
- Shift-Left Support Strategy: Move issue resolution closer to the end-user through self-service portals and a robust, well-maintained knowledge base, often managed using Knowledge-Centered Service (KCS).
Part 4: Measuring Success and Charting the Future
Chapter 10 & 11: Performance, Maturity, and Challenges
A data-driven approach is essential to demonstrate value and guide improvement.
- KPI Dashboard: Track metrics that matter, connecting technical performance to business outcomes. Key metrics include the “DORA metrics”: Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR), Change Failure Rate, Deployment Frequency, and Lead Time for Changes.
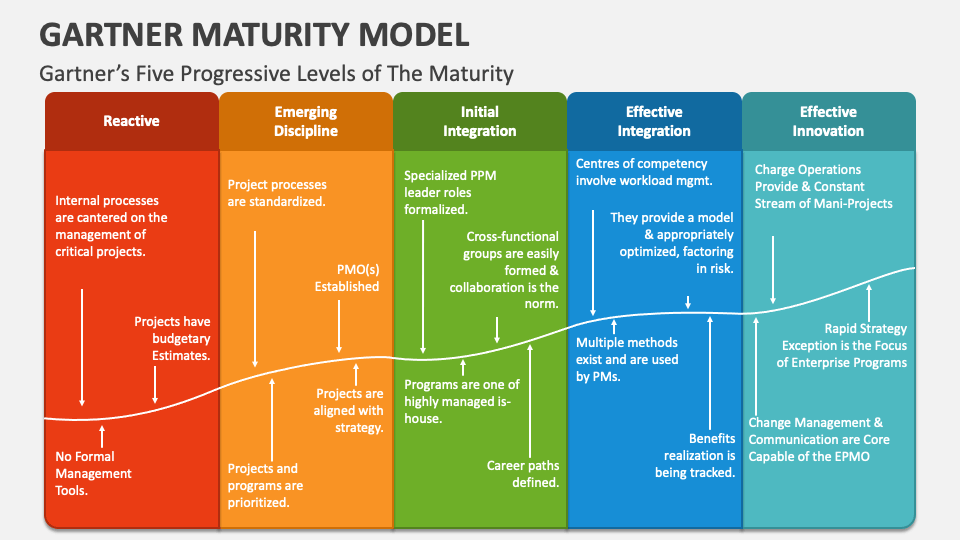
- Maturity Models: Use frameworks like the Gartner I&O Maturity Model to assess capabilities across People, Process, Technology, and Business Management, identifying areas for improvement.
- Common Challenges: Proactively address pitfalls such as fragmented automation, cultural resistance to change, and managing technical debt.
Chapter 12: The Strategic I&O Roadmap
Synthesize the playbook into a multi-year strategic roadmap to communicate vision and guide execution.
- Year 1 – Foundational Stability & Automation: Focus on establishing the basics: implement a hybrid governance framework, deploy IaC for critical services, establish a foundational observability platform, and gain cloud cost visibility.
- Year 2 & Beyond – Scaling Value & Driving Innovation: Scale capabilities by launching an Internal Developer Platform (IDP), implementing SRE for key services, expanding observability, and maturing the FinOps practice.